Translate this page into:
Late onset vitiligo and audiological abnormalities: Is there any association?
2 Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University; Department of Otolaryngology, Zain Hospital, Kuwait
Correspondence Address:
Nawaf Al-Mutairi
P.O. Box 280, Farwaniya, 80000
Kuwait
| How to cite this article: Al-Mutairi N, Al-Sebeih KH. Late onset vitiligo and audiological abnormalities: Is there any association?. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2011;77:571-576 |
Abstract
Background: There is scarce published data on late onset vitiligo. All the studies showing association of audiological abnormalities have been done on younger age group of patients. Aim: To study the clinical characteristics of the patients with late onset vitiligo. Also, to investigate the audiological abnormalities seen in these patients and compare them with age and sex matched healthy volunteers. Methods: One hundred and ninety-seven consecutive patients developing vitiligo after the age of 40 were studied. These patients were examined for the audiological abnormalities, and compared with those seen in age and sex matched healthy volunteers. Results: Vitiligo started between 40 and 50 years of age in 68.02% of our patients. Vitiligo vulgaris was the commonest clinical pattern, and most patients reported onset of their vitiligo on the upper extremities. Fifty four had diabetes mellitus, 19 patients had autoimmune thyroid diseases, and 32 showed hypoacusis on audiometric examination. Eighteen controls (age and sex matched healthy volunteers) also showed hypoacusis. The difference in frequency was not significant (22.37% vs 18%, χ2 - test, P > 0.05). The sensorineural type of audiologic impairment was more commonly seen both in patients as well as in controls. Conclusion: Late onset vitiligo was not found to have statistically significant association with audiological abnormalities in this study.Introduction
Vitiligo is a common, acquired, pigmentary disorder of skin and hair resulting from the destruction of functional melanocytes. It is characterized by well-circumscribed, asymptomatic depigmented macules. It affects all the ethnic groups and has a worldwide occurrence of 0.3% to 1.0%. [1] It can develop at any age, but most commonly occurs in the younger age group. Little published data on the characteristics of late onset vitiligo exists. [2],[3] The melanocytes originate from the neural crest, and they are located in the epidermis, hair bulbs of the skin, the uveal tract and retinal pigment epithelium of the eye, the inner ear, and the leptomeninges. The concept of "melanocytes organ" has been proposed. The mechanism destroying the melanocytes in the skin could also affect the other melanocyte harboring organs. Several ocular [4],[5] and audiological abnormalities have been reported [6],[7],[8],[9] in patients with vitiligo. All the studies showing association of audiological abnormalities have been done on younger age group of patients. The patients of more than 50 years of age had in fact been excluded in one of the study. [10] However, late onset vitiligo has been found to be more strongly associated with other autoimmune diseases. There are no studies on association of auditory abnormalities in late onset vitiligo. We carried out this case control study to find out, if there is any association of audiological abnormalities in patients with late onset vitiligo (age of onset >40 years).
Methods
All new patients of vitiligo, having onset of the disease after the age of 40 years, attending our OPD were enrolled in this prospective study. The study was done from January 2005 to December 2008. Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients and controls after a detailed explanation of the purpose and methodology to be used in the study. The diagnosis of vitiligo was made by experienced dermatologists, and was essentially clinical. The protocol for this study was approved by the hospital′s ethics committee. A standardized clinical proforma was used to record the history and clinical findings for all the patients.
A complete history regarding age, family history, age and site of onset, progression, concurrent illnesses, and treatment taken was noted. A thorough clinical examination was done, and the site and pattern of the lesions was noted. Presence of leukotrichia, Koebner′s phenomenon, and halo nevi were also noted. Screening was done for autoimmune and endocrine disorders by history, clinical examination, and relevant laboratory investigations; these disorders included thyroid disease, diabetes mellitus, pernicious anemia, Addison′s disease, connective tissue diseases, and alopecia areata. The clinical and tympanometric examination was done by an otorhinolaryngologist for the exclusion of external, and middle ear pathologies. Otoscopic and audiometric examinations were performed for both ears in all the patients. Investigations including hemoglobin level, total and differential leukocyte counts, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, peripheral smear, blood sugar, T3, T4, TSH, anti-thyroid antibodies (antithyroglobulin and antimicrosomal antibodies), fluorescent antinuclear antibodies were done for all patients. Audiometric examination was done for 143 patients (197 minus 54 diabetic patients) using a pure tone audiometer. Pure tone thresholds were determined for each ear at the frequencies of 250−8000 Hz for air conduction and 250−4000 Hz for bone conduction. The level of hearing impairment was assessed according to the 1964 International Standards Organization hearing threshold parameters, i.e., normal: inability to hear at 10−20 db, mild deafness: inability to hear at 21−40 db, and moderate deafness: inability to hear at 41−55 db.
Exclusion criteria
They included a history or evidence of audiological disease, familial hearing loss, ototoxic drug intake, chronic exposure to noise (e.g., industrial workers, environmental noise pollution, etc.), head injury.
Controls
For the purpose of evaluation of audiological abnormalities, one hundred age and sex matched healthy volunteers were taken as controls. None of the control was known to be suffering from any vascular or neurological disease, and also none of them had any history of ear disease. All of them were subjected to audiological examination by an otorhinolaryngologist to rule out any disease of external or middle ear, and were subsequently evaluated by audiometric examinations using same settings as it had been used for the patients.
Statistical methods used
Data was analyzed by statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) software. The χ2 -test was used to compare the rate of audiological abnormalities between cases and controls.
Results
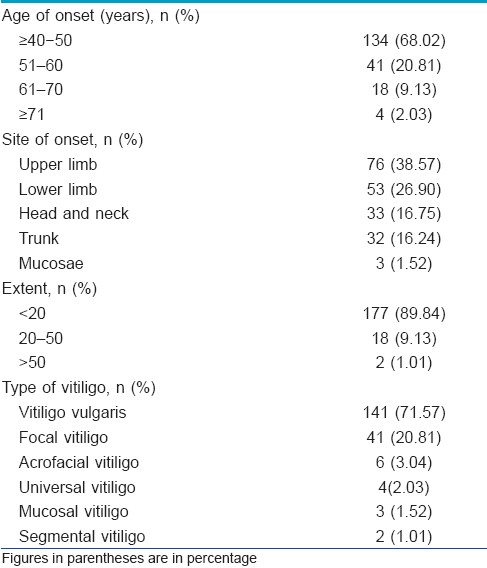
According to the study criteria, one hundred and ninety-seven (197) patients having onset of vitiligo after 40 years of age seen between January 2005 and January 2009, were included in the study. There were 95 (48.22%) males and 102 (51.77%) females. The age and sex distribution of the patients is given in [Table - 1]. The age of onset of vitiligo ranged from 40 years to 75 years [Table - 2]. In most of the patients (134;68.02%), vitiligo started between 40 and 50 years of age; 41 (20.81%) patients reported onset of vitiligo between the age of 51 and 60 years; 18 (9.13%) between 61 and 70 years, and 4 (2.03%) patients at >70 years of age. Duration of disease at the time of presentation ranged from 4 months to 15 years with a mean of 4.3 ± 3.5 years.
Vitiligo affecting first-degree relatives (parents/brother/sister) or second-degree relatives (grandparents/maternal and/or paternal uncle or aunt) was reported by 33 (16.75%) patients. Of these 33 patients, seven had more than one family member suffering from the disease.

 |
| Table 2: Age and site of onset, extent and types of vitiligo |
Vitiligo vulgaris was the most common type, and was seen in 141 (71.57%) patients followed by focal in 41 (20.81%), acrofacial in 6 (3.04%), universal in 4 (2.03%), mucosal in 3 (1.52%), and segmental in 2 (1.01%) patients. Besides the mucosal form of vitiligo, associated involvement of mucosae was seen in 24 patients with other clinical variants of vitiligo [Table - 2].
One hundred and seventy-seven (89.84%) of the patients had 5-20% of body area involvement. The most common site of onset was the upper limbs, followed by the lower limbs, the head and neck, the trunk, mucous membranes, and the flexures [Table - 2]. Vitiligo was stable in 141 (71.57%) patients.
Leukotrichia was observed in 88 (44.67%) patients and koebnerization in 33 (16.75%) patients. None of the patients had halo nevi. Other associated conditions seen in our patients are summarized in [Table - 3]. Seventy eight (39.59%) patients with vitiligo had other autoimmune diseases. Seventy three (93.58%) of the 78 patients with associated autoimmune diseases had generalized vitiligo. The three most common associated autoimmune disease seen in our patients included diabetes mellitus in 54 (69.23%); followed by 19 (24.35%) with autoimmune thyroid disease; alopecia areata in 11(14.1%) patients; other minor associated conditions included rheumatoid arthritis in 6 (7.69%) patients; pernicious anemia in 3 (3.84%) patients, and Addison′s disease in 2 (2.56%) patients. More than one associated autoimmune endocrine disorder was seen in 17 patients. Family history of autoimmune diseases was higher in the first-degree relatives than the second-degree relatives (20.3% vs. 14.21%). In addition to the 11 patients with alopecia areata, 27 patients had other associated skin disorders. It included eczema in 19 patients, psoriasis in 4 patients, lupus erythematosus in 3 patients, and lichen planus in 1 patient.

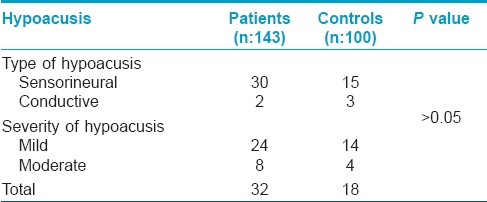
Though none of the patients complained of deafness, but on audiometric examination of 143 (197 minus 54 diabetic patients), hypoacusis was found in 32 (22.37%) patients. In the control group, hypoacusis was seen in 18 (18%) subjects. Hypoacusis was seen in both the sexes, and in all age groups in both patients and controls. The relation of the type of vitiligo to hypoacusis is shown in [Table - 4]. The type and severity of hypoacusis is shown in [Table 5]. Hypoacusis was mild in 24 patients and moderate in 8 patients. Out of the 32 patients showing hypoacusis, 30 (93.37%) had hypoacusis of sensorineural type.

Discussion
Vitiligo is a disorder of pigmentation characterized by the presence of milky-white skin macules. The term vitiligo has evolved from the Latin word vitium, meaning fault, or vitelius meaning spotted calf. [11] Most published reports on vitiligo include patients of all ages and some include only children and adolescents. On pubmed search, we could find only two reports focusing on vitiligo with onset in adulthood. [2],[3] All reports available in the literature indicate that most of the cases of vitiligo are primarily acquired early in the life. [11] However, there is a subset of patients with onset of vitiligo after adulthood.
There was no statistical difference between the number of male and female patients in our study, and the female to male ratio was 1.04:1. Slight preponderance of females in adult onset vitiligo has been reported [2],[3] in the past. Thirty three (16.75%) patients gave a positive family history (immediate family and extended family included) of vitiligo. Higher incidence of consanguineous marriages in our part of world increases the importance of associated genetic factors, in any given disease. Analyzing the age of onset of the patients in our study, we observed that 68.02% of patients developed vitiligo between the ages 40 and 50 years, while 31.98% had developed vitiligo after the age of 50 years. A study of Romanian population indicated that age of onset of vitiligo is determined almost completely by nongenetic environmental factors. [12] Thus, whereas a major gene or genes seems to govern susceptibility to vitiligo, actual onset of disease depends on the exposure of genetically susceptible individuals to the environmental triggers. [13] Another model suggested that there may in fact be two coexisting modes of inheritance for vitiligo depending on the age of onset. In patients with early onset vitiligo (before the age of 30), vitiligo inheritance most closely followed a dominant mode of inheritance with incomplete penetration. However, a predisposition to vitiligo resulting from a recessive genotype and exposure to certain environmental triggers appeared to explain the inheritance pattern of late onset vitiligo (after 30 years of age). [13],[14]
Vitiligo vulgaris was the commonest clinical presentation seen in our patients, and segmental vitiligo was seen in only 2 (1.01%) of our patients. In contrast, segmental vitiligo forms a significantly large subgroup (8−32.5%) of patients with childhood vitiligo. [15],[16] The upper limbs were reported as the most common site of onset of vitiligo in most of our patients, followed by the lower limbs. The exact significance of this observation is difficult to appreciate. Routine and often repeated trauma to the upper limbs and the lower limbs in adults engaged in various occupations may predispose these areas to develop vitiligo lesions more easily in genetically predisposed persons. Leukotrichia was seen in 88 (44.67%) of our patients and koebnerization was observed in 33 (16.75%) patients. Halo nevus was not observed in any of our patients. Halo nevi have also not been referred to in the South Korean study. [16] They are reported to occur in 0.5% to 14% of vitiligo patients of all age groups. [17] We believe that halo nevi coexisting with vitiligo lesions are not commonly seen in adult-onset vitiligo.
Vitiligo is characterized by progressive loss of melanocytes from the epidermis accompanied by elevated titers of anti-melanocyte antibodies and inflammatory skin infiltrates. Recently obtained evidence strongly indicates that this pigmentary disorder is an autoimmune disease. [18] Associated autoimmune/endocrine disorders were present in 78 (39.59%) of our vitiligo patients. There was a high incidence of diabetes mellitus, seen in 54 (69.23%) patients; followed by 19 (24.35%) with autoimmune thyroid disease; alopecia areata in 11 (14.1%) patients. Also, rheumatoid arthritis, pernicious anemia, and Addison′s disease were seen in some of our patients. Vitiligo in adults is quite strongly associated with a number of autoimmune disorders, including alopecia areata, diabetes mellitus, pernicious anemia, Addison′s disease, and Hashimoto′s thyroiditis. [11],[19] Those patients with adult onset vitiligo have an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases, and also that auto-antibodies against different organ systems can be present in these patients without clinical correlation. [11] Another study found that the frequency of six autoimmune disorders is significantly higher in vitiligo probands and their first-degree relatives; vitiligo itself, autoimmune thyroid disease, pernicious anemia, Addison′s disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, and probably inflammatory bowel disease. [20]
Vitiligo and diabetes may have a causal relationship and both are associated with autoimmunity. [21] The occurrence of vitiligo in diabetes may be as a result of a basic autoimmune disturbance in the same patient affecting two organ systems. Both diabetes and vitiligo are associated with HLA DR3 and HLA DR4. Longstanding diabetes mellitus may cause an injury to melanocytes resulting in the release of an antigenic substance, antimelanocyte antibody formation, inhibition of melanogenesis and occurrence of vitiligo. Multiple pathogenetic mechanisms may be involved. The products of oxidative stress, free radical generation and release of various growth factors may be cytotoxic, affecting melanogenesis. Hence, diabetes mellitus should be screened in all cases of late onset vitiligo. [22] Extrinsic factors may play a role in vitiligo; many patients attribute the onset of their disease to illness or emotional stress. These hypotheses may not be separate, indicating vitiligo to be a heterogeneous disease encompassing multiple etiologies. [23]
The embryonic origin of human melanocytes is from the neural crest, and they are located in the epidermis, hair bulbs of the skin, the uveal tract and retinal pigment epithelium of the eye, the inner ear and the leptomeninges. [24],[25] The mechanism destroying the melanocyte in the skin could also affect other melanocytic organs. [26] Several ocular [4],[5] and audiological abnormalities of hearing [6],[7],[8],[9] have been reported in patients with vitiligo. The affection of extracutaneous melanocytes in some vitiligo patients suggests that systemic immunological reactions directed at pigment cells might play a role in the development of the disease. [27] It is believed that in vitiligo, synchronic with the loss of epidermal melanocytes, melanin-containing cells in the inner ear lose their preventive function and predispose the inner ear to be affected by environmental damaging factors and subsequently lead to sensorineural hearing loss. [28] Our results show that out of 143 adult patients with vitiligo 32 (22.37%) had hypoacusis. The patients found to have hypoacusis were distributed among all clinical types of vitiligo. Majority of our patients showing hypoacusis had sensorineural type of impairment (30 patients). However, on comparing the findings of audiometric examination to age and sex matched group of healthy volunteers, there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups. Hence, we concluded that in contrast to the association noticed in early onset vitiligo, late onset vitiligo does not seem to be significantly associated with audiological abnormalities. This finding may further support the belief that adult onset vitiligo behaves differently from early onset disease. Although it is more often associated with systemic disease and endocrinological abnormalities, there seems to be no evidence of increased association with audiological abnormalities.
| 1. |
Majumder PP. Genetics and prevalence of vitiligo. In: Hann SK, Norlund JJ, editors. Vitiligo: A monograph on the basic and clinical science. 1 st ed. Bangalore: Blackwell Science; 2000. p. 18-20.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 2. |
Mason CP, Gawkrodger DJ. Vitiligo presentation in adults. Clin Exp Dermatol 2005;30:344-5.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 3. |
Dogra S, Parshad D, Handa S, Kanwar AJ. Late onset vitiligo: A study of 182 patients. Int J Dermatol 2005;44:193-6.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 4. |
Biswas G, Barbhuiya JN, Biswas MC, Islam MN, Dutta S. Clinical pattern of ocular manifestations of vitiligo. J Indian Med Assoc 2003;101:478-80.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 5. |
Cowan CL Jr, Halder RM, Grimes PE, Chakrabarti SG, Kenney JA Jr. Ocular disturbances in vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol 1986;15:17-24.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 6. |
Tosti A, Bardazzi F, Tosti G, Monti L. Audiologic abnormalities in cases of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol 1987;17:230-3.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 7. |
Orecchia G, Marelli MA, Fresa D, Robiolio L. Audiological disturbances in vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol 1989;21:1317-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 8. |
Ozuer MZ, Sahiner T, Aktan S, Sanli B, Bayramoðlu I. Auditory evoked potentials in vitiligo patients. Scand Audiol 1998;27:255-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 9. |
Sharma L, Bhawan R, Jain RK. Hypoacusis in vitiligo. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2004;70:162-4.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 10. |
Aydogan K, Turan OF, Onart S, Karadogan SK, Tunali S. Audiological abnormalities in patients with vitiligo. Clin Exp Dermatol 2006;31:110-3.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 11. |
Kovacs SO. Vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998;38:647-66; quiz 667-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 12. |
Birlea SA, Fain PR, Spritz RA. A Romanian population isolate with high frequency of vitiligo and associated autoimmune diseases. Arch Dermatol 2008;144:310-6.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 13. |
Arcos-Burgos M, Parodi E, Salgar M, Bedoya E, Builes J, Jaramillo D, et al. Vitiligo: Complex segregation and linkage disequilibrium analyses with respect to microsatellite loci spanning the HLA. Hum Genet 2002;110:334-42.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 14. |
Finco O, Cuccia M, Martinetti M, Ruberto G, Orecchia G, Rabbiosi G. Age of onset in vitiligo: Relationship with HLA supratypes. Clin Genet 1991;39:48-54.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 15. |
Al-Mutairi N, Sharma AK, Al-Sheltawy M, Nour-Eldin O. Childhood vitiligo: A prospective hospital-based study. Australas J Dermatol 2005;46:150-3.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 16. |
Cho S, Kang HC, Hahm JH. Characteristics of vitiligo in Korean Children. Pediatr Dermatol 2000;17:189-93.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 17. |
Handa S, Kaur I. Vitiligo: Clinical findings in 1436 patients. J Dermatol 1999;26:653-7.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 18. |
van den Wijngaard R, Wankowicz-Kalinska A, Pals S, Weening J, Das P. Autoimmune melanocyte destruction in vitiligo. Lab Invest 2001;81:1061-7.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 19. |
Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Vitiligo. Cutis 1997;60:239-44.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 20. |
Alkhateeb A, Fain PR, Thody A, Bennett DC, Spritz RA. Epidemiology of vitiligo and associated autoimmune diseases in Caucasian probands and their families. Pigment Cell Res 2003;16:208-14.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 21. |
Olasode OA. Why vitiligo in diabetes? Egypt Dermatol Online J 2005;1:8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 22. |
El-Mofty AM. Vitiligo and psoralens. New York: Pergamon Press Inc; 1968. p. 24.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 23. |
Freiman A, Gratton D. Vitiligo. Dermatology Rounds 2005;4. Available from: http://www.dermatologyrounds.ca. [Last accessed on 2011 Feb 15].
[Google Scholar]
|
| 24. |
Halaban R, Heberi DN. Biology of melanin. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, editors. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. 6 th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003. p. 127-48.
th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003. p. 127-48.'>[Google Scholar]
|
| 25. |
Goldgeie MH, Klein LE, Klein-Angerer S, Moellmann G, Nordlund JJ. The distribution of melanocyte in the leptomeninges of the human brain. J Invest Dermatol 1984;82:235-8.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 26. |
Ortonne JP, Bose SK. Vitiligo: where do we stand? Pigment Cell Res 1993;6:61-72.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 27. |
Kemp E, Waterman E, Weetman A. Immunological pathomechanisms in vitiligo. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press; 2001. p. 1462-3994.
[Google Scholar]
|
| 28. |
Steel KP, Barkway C. Another role for melanocytes: Their importance for normal stria vascular is development in the mammalian inner ear. Development 1989;107:453-63.
[Google Scholar]
|
Fulltext Views
12,099
PDF downloads
1,778





